Overview: Establishing a Family Office in Singapore

The number of family offices worldwide have grown significantly, this trend coincides with the phenomenal economic rise of Asia. The data shows that the accumulation of wealth by families in Asia is faster than in any other region of the world. Family offices have therefore naturally developed to manage this wealth expansion Given the growing wealth in Asia.
Singapore has witnessed the rapid growth of its wealth management industry. This has led to the development of a supportive and sophisticated financial, legal, tax, and human resource infrastructure. As a result, the island nation is now home to many sophisticated wealth management entities. From 2017 to 2022, the number of new family offices that have been set up in Singapore have increased from 100 to over 700. The major reason for this rise is regulatory changes. In March 2019, MAS and the Singapore Economic Board (EDB) jointly established the Family Office Development Team (FODT) to enhance Singapore’s competitiveness as a global wealth management and family office hub.
There are many reasons for setting up a family office although the typical reason is that families are looking to in-source their fund management functions or at the minimum be more involved in the management of their financial assets. As these families accumulate financial capital, their needs and responsibilities get more complex and challenging to address. Several forms of family office services have existed for many years, often seeing wealthy families organising an inner circle of trusted advisors to centralise the management of their wealth.
What is a Family Office?
A family office is generally a company that provides a number of services for a wealthy family such as asset management. A key function of the typical family office is the management of the assets of one or more families; these assets may be held by captive investment vehicles which from part of a broader wealth planning structure.
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) defines a single-family office (SFO) as one that provides services to members of the same family, This may be contrasted with a multi-family office (MFO) which provides services to members of different families.
Why Singapore?
Singapore has increasingly become the jurisdiction of choice for the set-up of a family office and family funds. Aside from hosting a deeply diverse pool of wealth management talent and having a variety of attractive tax incentive schemes to benefit from, Singapore is renowned for its political and economic stability and robust legal infrastructure, making it the choice hub for ultra-high-net-worth families seeking to set up their family office.
Singapore is also a place where many wealthy individuals and their trusted advisors are happy to live and work because it is well connected internationally with direct flight to most investments. A Singapore family office may sponsor employment passes and may even be used as part of an application for permanent residency by family members under Global Investor Programme which is administered by the EDB.
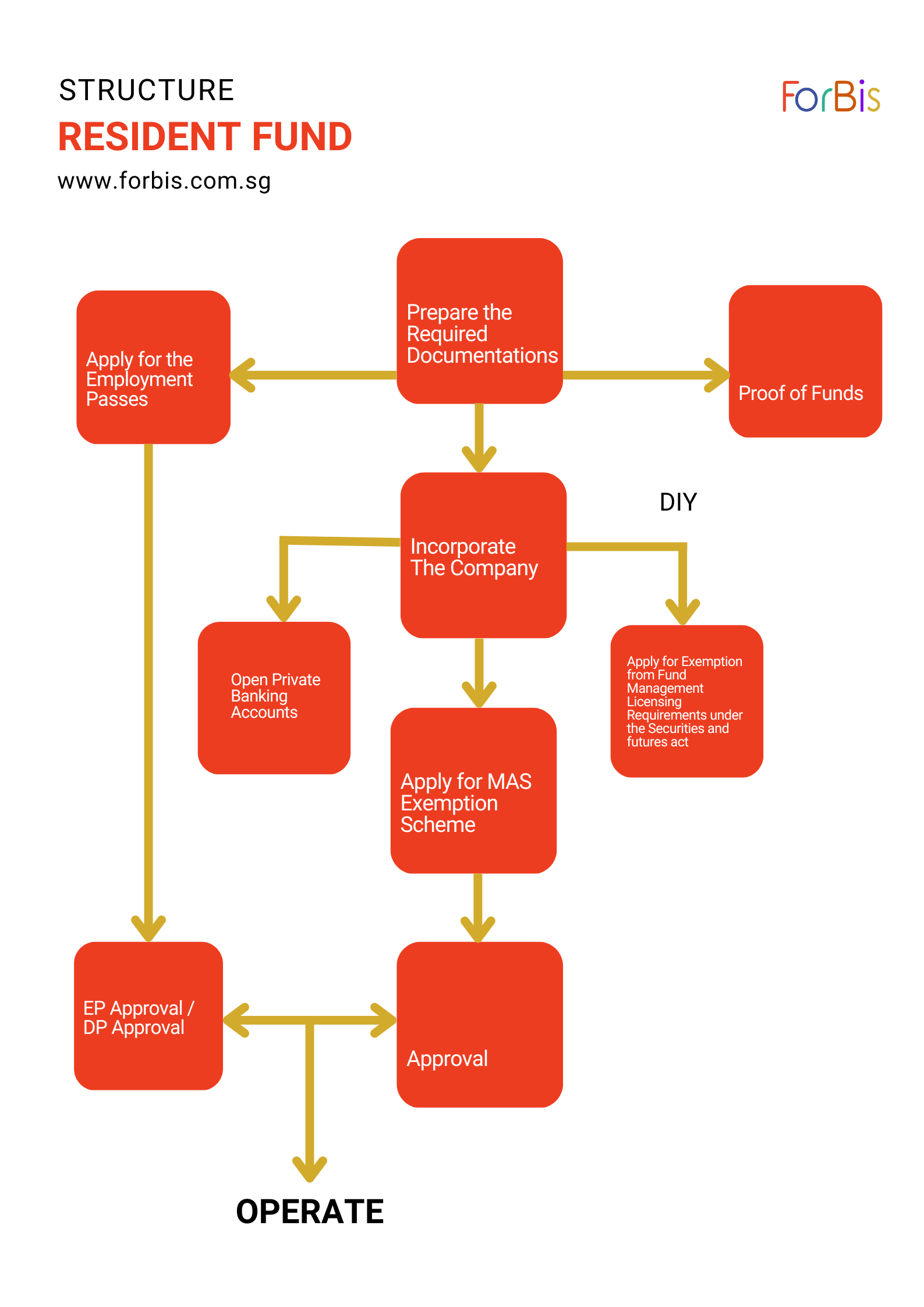
Setting up and structure of Family Office
The setting up of a family office is typically coupled with the setting up of a family fund. The set-up of a family fund institutionalises the holding structure for the family’s assets, facilitates succession planning and creates a more efficient and transparent structure. Family office also brings renewed relevance as it broadens its role to a more diverse landscape of financial and non-financial needs that include private wealth management, family governance, legacy planning, knowledge and cultural transfer, philanthropy, investment management, insurance, and management of family-owned businesses amidst global volatility and the emergence of new technologies.
These areas must be considered in the broader context of individual members’ desires, family perceptions, as well as the macroeconomic and regulatory landscape the families operate within.
The structure described for that qualifies for an Investment Management of Family Offices is shown in the diagram below.
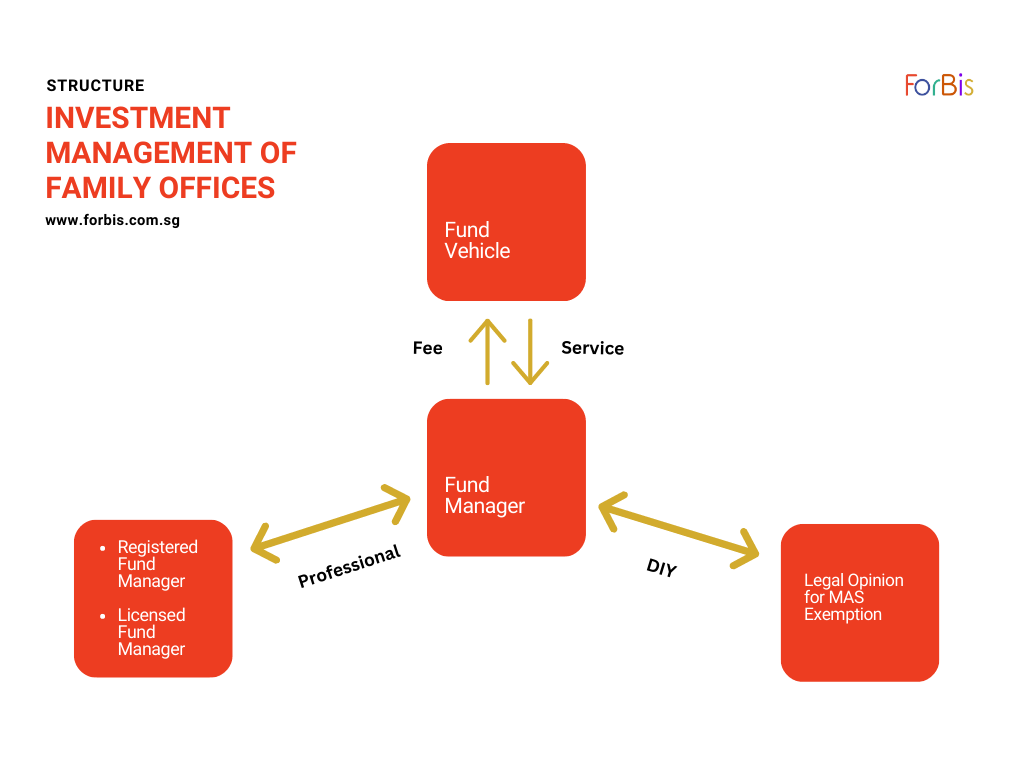
The baseline structure would involve a holding company directly owning both the Family Office and the fund entity. The holding company and fund entity can be, although they need not be, Singapore companies. Unlike many offshore jurisdictions, Singapore does not have any general economic substance laws. However, to qualify for fund management tax incentives under the Income Tax Act, a fund manager must have real operations in Singapore.
